1 长春理工大学光电工程学院,吉林 长春 130022
2 中国人民解放军总医院耳鼻咽喉头颈外科医学部,北京 100039
3 国家耳鼻咽喉疾病临床医学研究中心,北京 100039
为了实现从前鼻孔进镜对鼻黏膜表面进行直接显微成像,从而进行无创性观察和测量在体鼻纤毛运动,设计了一种能够分辨鼻纤毛,并且带有30°视向角的变倍硬性显微内窥镜。所设计的硬性内窥镜系统物方数值孔径为0.15,分辨率为272 lp/mm,工作距离为3.00 mm,视向角为30°,物面高度为0.40 mm,系统总长度为205.62 mm,物方口径为4.65 mm,放大倍率为6×~10×。此鼻黏膜纤毛显微内窥镜将可以避免取材造成的纤毛功能损害和受试者痛苦,极大地提高纤毛相关疾病的临床诊断能力,成为助益纤毛领域科研和临床工作的重要突破。
医用光学 鼻黏膜纤毛 硬性内窥镜 视向角 变倍 高分辨率
长春理工大学光电工程学院,吉林 长春 130022
针对传统硬性工业内窥镜在炉窑内部监测视野小、分辨能力低和工作距离短的问题,设计一种大靶面、长工作距的高清工业内窥镜。采用一体化设计思路,设计内容包含广角像方远心物镜系统和对称式消像差棒镜中继系统。所设计的高清工业内窥镜的光学数为6、视场角为103°、光学长度为1040 mm、光学外径不大于26 mm、靶面对角线长度为16 mm、系统像方远心度不大于1.8°,且调制传递函数不小于0.2@160 lp/mm。实验结果显示,所设计的工业内窥镜在40 cm至无穷远范围内可清晰成像,并且在5 m远处可分辨10 mm的线对宽度,角分辨率为8.73 C/(°)。该内窥镜的设计优势:系统的接收器靶面尺寸大,物方分辨率高;对称式消像差棒镜中继系统的延展性好,光通量高;物像以远心的形式衔接,光线传播平滑,像面照度均匀。
光学设计 工业内窥镜 中继系统 F数 光学学报
2022, 42(22): 2222001
1 清华大学机械工程系摩擦学国家重点实验室, 北京 100084
2 清华大学精密超精密制造装备及控制北京市重点实验室, 北京 100084
根据扫描干涉场曝光的特点,针对光刻胶层内曝光量的驻波效应,建立了动态曝光模型。基于快速推进法建立了显影模型,得到了光栅掩模槽形的演变规律。为减弱驻波效应的影响,提出了一种抗反射层最优厚度的设计方法。仿真结果表明,建立的曝光和显影模型能有效预测光栅掩模的槽形轮廓,同时可优化抗反射膜的厚度。
光栅 扫描干涉场曝光 曝光模型 显影模型 快速推进法 驻波效应
1 清华大学机械工程系摩擦学国家重点实验室, 北京 100084
2 清华大学机械工程系精密超精密制造装备及控制北京市重点实验室, 北京 100084
高斯光在远离束腰位置能得到直线度极高的干涉条纹,基于此提出了一种基于远场干涉的新型扫描干涉场曝光(SBIL)系统。建立了条纹相位非线性误差关于高斯光束腰半径、入射角度及束腰到基底距离的解析表达式。通过数值仿真,详细分析了条纹相位非线性误差与上述参数的关系。研究结果表明,该光学系统可以有效地将条纹相位非线性误差限制在纳米量级,并具有光路简洁、装调误差宽容度较高的优点。适当缩短束腰到基底的距离,可有效解决曝光光斑边界处条纹相位非线性误差恶化的问题。
衍射 扫描干涉场曝光 干涉条纹 高斯激光 空间滤波器 菲涅耳衍射
1 清华大学机械工程系摩擦学国家重点实验室, 北京 100084
2 清华大学精密超精密制造装备及控制北京市重点实验室, 北京 100084
3 东风商用车技术中心基础技术研究室, 湖北 武汉 430056
扫描干涉场曝光(SBIL)系统中曝光效果与工件台的运动性能密切相关。为了制作纳米精度的大面积平面光栅,工件台采用了粗微叠层结构设计,其中微动台是实现工件台运动精度的关键。基于SBIL原理,推导了干涉条纹周期测量精度与曝光对比度的关系。针对移动分光镜测量干涉条纹周期的方法,结合周期测量精度需求,分析了微动台定位精度指标,提出了实现微动台x、y、θz三个自由度定位精度的控制器设计方法,并在微动台系统上进行了实验验证。结果表明,微动台x方向定位精度可达±1.51 nm,y方向定位精度可达±5.46 nm,θz定位精度可达±0.02 μrad,可以满足SBIL的需求和干涉条纹周期测量的精度要求。
测量 扫描干涉场曝光 微动台 条纹周期测量精度 相位锁定 光学学报
2017, 37(10): 1012006
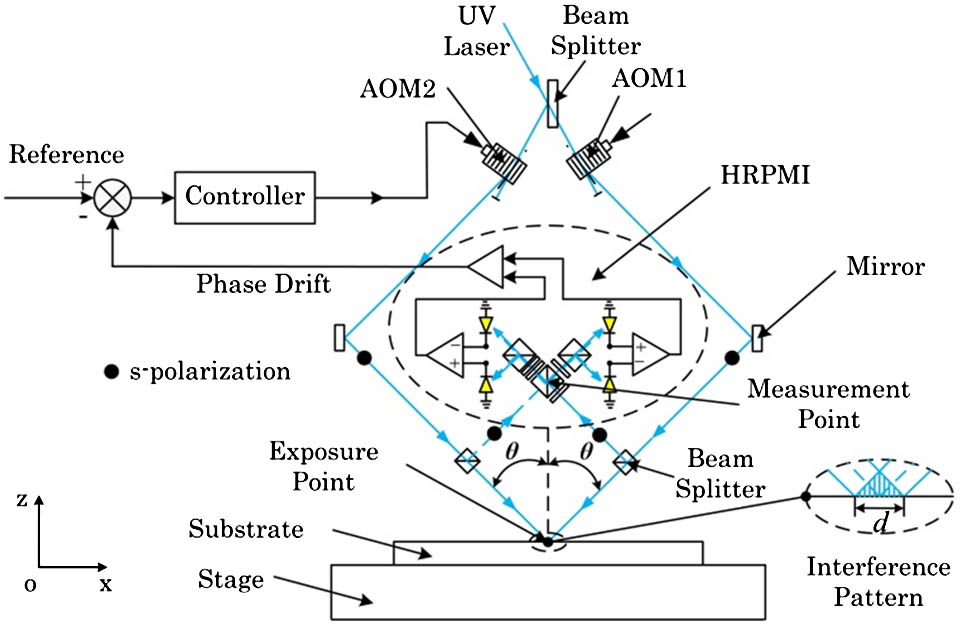
Author Affiliations
Abstract
State Key Laboratory of Tribology, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
We present a novel homodyne frequency-shifting interference pattern locking system to enhance the exposure contrast of interference lithography and scanning beam interference lithography (SBIL). The novel interference pattern locking system employs a special homodyne redundant phase measurement interferometer (HRPMI) as the sensor and an acousto-opto modulator (AOM) as the actuator. The HRPMI offers the highly accurate value as well as the direction recognition of the interference pattern drift from four quadrature interference signals. The AOM provides a very fine resolution with a high speed for phase modulation. A compact and concise system with a short optical path can be achieved with this new scheme and a small power laser head in tens of microwatts is sufficient for exposure and phase locking, which results in a relatively low-cost system compared with the heterodyne system. More importantly, the accuracy of the system is at a high level as well as having robustness to environmental fluctuation. The experiment results show that the short-time (4 s) accuracy of the system is ±0.0481 rad(3σ) at present. Moreover, the phase of the interference pattern can also be set arbitrarily to any value with a high accuracy in a relatively large range, which indicates that the system can also be extended to the SBIL application.
000.2170 Equipment and techniques 050.1950 Diffraction gratings 120.3180 Interferometry 220.3740 Lithography Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(6): 061201
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Devices and Systems of Ministry of Education and Guangdong Province, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen, 518060, China
Two promising post-treatment techniques, i.e. applying tensile strain and rising temperature, are demonstrated to enhance the mode-coupling efficiency of the CO2-laser-induced long period fiber gratings (LPFGs) with periodic grooves. Such two post-treatment techniques can be used to enhance the resonant attenuation of the grating to achieve a LPFG-based filter with an extremely large attenuation and to tailor the transmission spectrum of the CO2-laser-induced LPFG after grating fabrication.
Long period fiber gratings Long period fiber gratings fiber Bragg gratings fiber Bragg gratings optical fiber sensor optical fiber sensor temperature temperature tensile strain tensile strain optical fiber device optical fiber device Photonic Sensors
2015, 5(4): 339
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Devices and Systems of Ministry of Education/Guangdong Province, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen, 518060, China
Photonic crystal fibers are usually divided into two different types of fibers: solid-core photonic crystal fibers (PCFs) and air-core photonic bandgaps fibers (PBFs). We presented the fabrication methods and applications of long period fiber gratings (LPFGs) written in these two types of photonic crystal fibers by use of a CO2 laser. A stain sensor with a high sensitivity was demonstrated by use of an LPFG written in solid-core PCFs. An in-fiber polarizer based on an LPFG was fabricated by use of a focused CO2 laser beam to notch periodically on a PCF. A novel LPFG was written in an air-core PBF by use of a CO2 laser to collapse periodically air holes in the fiber cladding.
Long period fiber gratings fiber Bragg gratings photonic crystal fibers photonic bandgap fibers CO2 lasers Photonic Sensors
2013, 3(3): 193





